 When it comes to toilet cleaners, consumer satisfaction hinges on more than just cleaning power. A superior toilet cleaner must be easy to apply, specifically when targeting hard-to-reach areas under the rim. Beyond the initial application, consumers typically look for two key visual cues.
When it comes to toilet cleaners, consumer satisfaction hinges on more than just cleaning power. A superior toilet cleaner must be easy to apply, specifically when targeting hard-to-reach areas under the rim. Beyond the initial application, consumers typically look for two key visual cues.
- Adhesion: The product must adhere to the surface of the toilet bowl, allowing for a longer contact time during cleaning.
- Visual Thickness: This plays a key role, as consumers often equate a thicker appearance with more effective cleaning.
Conversely, users are increasingly attentive to negative attributes such as the occurrence of fingering, where the cleaner may unevenly spread or streak, detracting from the perceived efficacy of the product.
 Basic viscometry is commonly employed when characterising these products. However, these instruments do not capture the non-Newtonian behaviour of these products. At the Centre for Industrial Rheology, we provide rapid access to advanced rheological insights to ensure you get a complete profile of your product’s performance.
Basic viscometry is commonly employed when characterising these products. However, these instruments do not capture the non-Newtonian behaviour of these products. At the Centre for Industrial Rheology, we provide rapid access to advanced rheological insights to ensure you get a complete profile of your product’s performance.
Additionally, our axial testing capabilities allow us to characterise nuanced insights through normal stress generation. These measurements can be used as a proxy for extensional behaviour, thereby enabling the prediction of properties such as stringiness and coating coverage. Complementing our bulk rheological methods, we utilise dynamic contact angle analysis on a tilt-table setup with a ceramic tile, intended to mimic the surface of a toilet bowl. This method can be used to explore the occurrence of fingering or streaking.
Comprehensive Characterisation of Toilet Cleaners
In this study, we compared two popular toilet cleaners, each uniquely marketed based on distinct benefits.
- Duck Deep Action Gel – specifically highlights its optimised design and formulation for superior reach under the toilet rim and effortless application.
- The Works Toilet Bowl Cleaner – promotes its strength in tackling stubborn, visually unappealing stains such as rust, limescale, and hard water deposits.
Rheological Characterisation of Toilet Cleaners
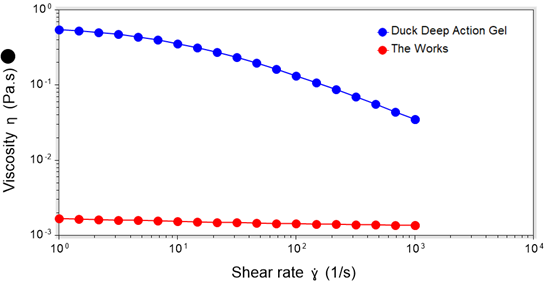
Figure 2 reveals the distinct rheological behaviours of both samples. The Works displays Newtonian behaviour, with viscosity remaining constant across the shear rate range tested. In contrast, Duck Deep Action Gel exhibits non-Newtonian, shear-thinning behaviour, where viscosity decreases as shear rate is increased. This is a beneficial attribute, as it allows the product to maintain sufficiently high viscosity at rest to cling to surfaces, while still flowing easily when pumped or dispensed. These performance attributes are only apparent when measuring viscosity across a range of shear rates.
Capturing The Extensional Behaviour of Toilet Cleaners
Normal stress is the axial stress generated within a fluid under shear, measured as the normal force per unit area exerted perpendicular to the surfaces in contact with the fluid. It is indicative of a fluid’s extensibility and hence a predictor of extensional viscosity. The normal stress data differ significantly between the two tested toilet cleaners.
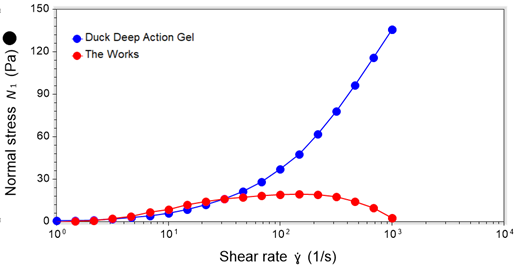
Duck Deep Action Gel shows a pronounced increase in normal stress as shear rate increases, showcasing a substantially higher normal stress compared to The Works. This notable increase suggests strong extensional behaviour, which may assist with forming a smooth, uniform coating across the toilet bowl.
However, a high normal stress may also carry potential drawbacks, particularly manifesting as stringing or tailing issues. Stringiness can cause messy application experiences when a consumer pumps the product out of the bottle. In addition to this, operational challenges can occur during the manufacturing process. In factory filling lines, stringing often leads to contamination, messy batches, and increased downtime for equipment cleaning, potentially impacting overall production efficiency. As such, it is important to carefully balance extensional behaviour to maximise product performance while minimising production and application drawbacks.
Dynamic Contact Angle Measurements for Toilet Cleaners
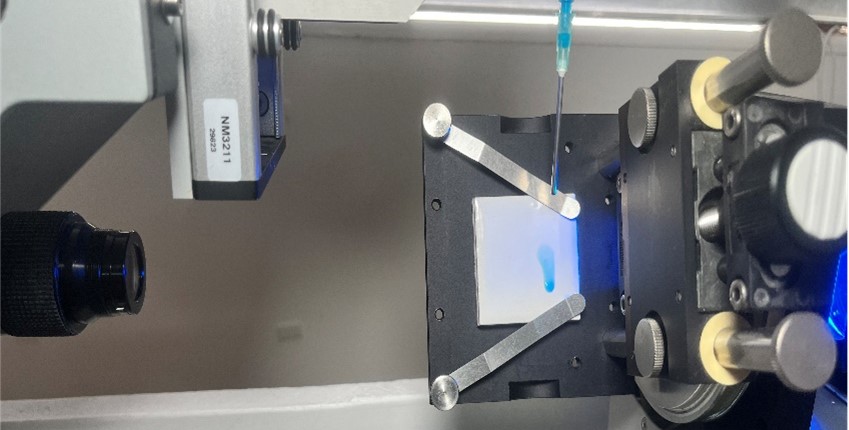
Dynamic contact angle analysis was used to investigate the occurrence of fingering, where a toilet cleaner spreads unevenly down a toilet bowl. A tilt-table setup with a ceramic tile substrate was used, intended to mimic a toilet bowl surface. Initially, a drop of the toilet cleaner is deposited on the ceramic tile. The table is then slowly tilted to increase the tilt table angle. By tracking both advancing and receding contact angles as the tilt increases, we get insights into droplet sliding or roll-off. Advancing contact angle reflects how the leading edge of the fluid spreads forward, and receding angle reflects how easily the trailing edge lets go, with the difference between these angles known as contact angle hysteresis.
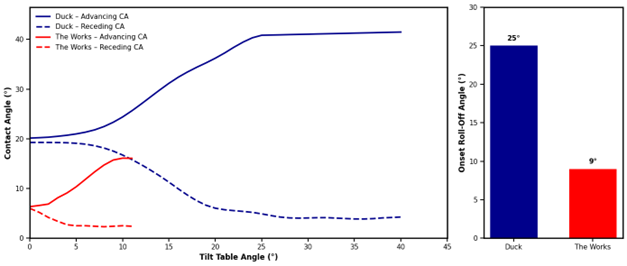
On a level surface, Duck’s advancing contact angle begins at 20° and climbs steadily past 40° as the substrate is tilted, while the receding angle drops to just below 5°. This results in a substantial contact angle hysteresis, indicating that the leading edge actively wets fresh ceramic while the trailing edge remains firmly pinned. Most notably, the roll-off angle is almost triple that of The Works, underscoring Duck’s superior ability to cling to vertical toilet bowl surfaces
In contrast, The Works’ advancing contact angle never exceeds 16°, and the receding angle drops below 3° almost immediately. The sample slides off the substrate rapidly, departing the field of view at a mere 11° tilt, far lower than the 40° stability observed with Duck. The resulting low hysteresis suggests that while the fluid momentarily wets the ceramic, it lacks the grip to maintain contact time. This rapid runoff often results in unstable flow, leading to the fingering and streaking commonly cited in consumer complaints.

Figure 6 visually reinforces the disparity in performance between the two formulations. Duck Deep Action Gel appears to cling to the surface better, whereas The Works appears to slide off more easily, with some apparent streaking occurring. Overall, while The Works achieves quick initial spreading, it lacks the necessary grip to maintain controlled, even coverage. Duck Deep Action Gel, however, exhibits better stability under tilt, offering the robust clinging performance required to minimise fingering.
Summary
This study underscores the importance of comprehensive rheological characterisation in the development of effective toilet cleaners. By combining advanced rheological testing with dynamic contact angle analysis, we provide the essential insights needed to optimise formulations. If you are looking to elevate your toilet cleaner formulations, contact us to discuss how we can support the characterisation of your product.

Related Article;
Household Products: Viscosity, Rheology and Interfacial Measurements
Dynamic Insights for a Sustainable Clean – The Future of Surfactant Performance in Detergency
Wasif Altaf serves as an Applications Specialist at the Centre for Industrial Rheology, leveraging a chemical engineering background (BEng) to bridge theory and practice. His work focuses on advanced rheological characterisation.
