Consumers expect household surface sprays to spray effortlessly with large surface coverage. However, optimising formulations for spraying processes remains a persistent challenge.
Relying on equilibrated surface tension data from methods such as optical and force tensiometry often provides an incomplete picture. The journey of a droplet, from the nozzle to wetting a surface, is a rapid event that unfolds in timescales of milliseconds. Utilisation of dynamic surface tension measurements from surface ages as short as 5ms provides relevant insights into behaviours that govern atomisation, droplet breakup, and surface wetting.
Differences Between Static and Dynamic Surface Tension Values
When a surface spray is ejected from a nozzle, new surfaces are created rapidly. Surfactant molecules must migrate and adsorb at the newly formed air-liquid interfaces. Static surface tension methods capture values after the interface has mostly stabilised, from around 1 second onwards.
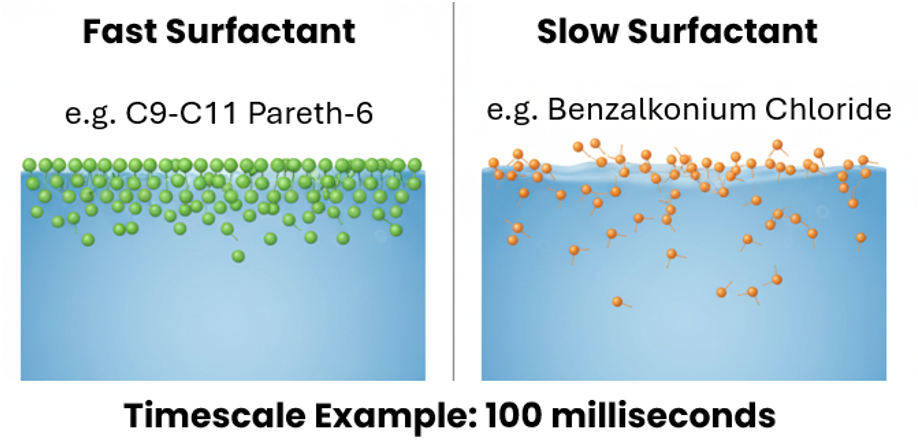
By contrast, dynamic surface tension measurements through bubble pressure tensiometry provide values from surface ages as short as 5 milliseconds. Analysis at such short timescales reveals insights into how quickly surfactants are migrating to these newly formed interfaces to reduce surface tension.
Capturing such data enables the differentiation of surfactant kinetics. For example, we can benchmark a faster-adsorbing non-ionic alcohol ethoxylate, such as C9-C11 Pareth-6, against a potentially slower-adsorbing cationic quaternary ammonium compound, such as Benzalkonium Chloride. For formulators, this ability to compare and benchmark surfactant kinetics for spray formulations is essential. It provides the exact tool needed to select and optimise a surfactant system, tailoring the dynamic surface tension profile to meet the precise demands of surface spray applications.
Contact us to discuss your requirements
Dynamic Surface Tension of Household Surface Sprays
In this study, we characterised multiple leading household surface sprays to benchmark their dynamic surface tension profiles.
- Dettol Power and Pure Kitchen
- Flash Kitchen
- Mr Muscle Platinum Kitchen
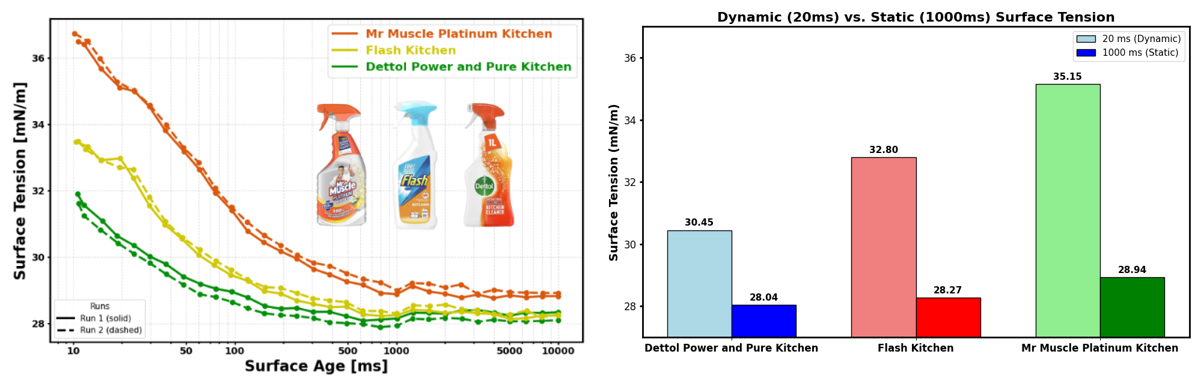
Figure 2 clearly illustrates the limitations of static measurements. The static surface tension values at 1000ms fail to differentiate significantly between the samples tested, whereas the dynamic data below this timeframe reveal more significant variations.
As droplet impact in spray applications typically occurs within 20 milliseconds, we compared values at this relevant timescale to those at 1000ms. The differences in values obtained at 20ms show that Dettol has a notably lower surface tension. This suggests superior wetting, and this may be imparting greater product performance compared to its counterparts.
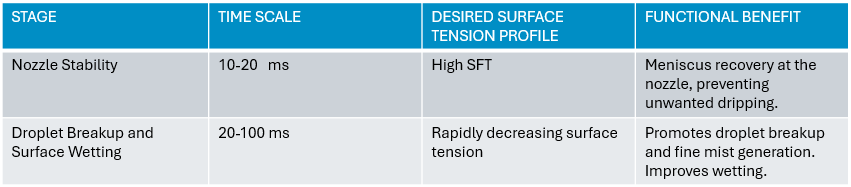
Beyond benchmarking formulations, there are key stages that present a distinct target for optimisation for formulators within a dynamic surface tension profile, summarised in Table 1 below.
Summary
While viscosity and static surface tension methods remain useful for general characterisation, dynamic surface tension values provide the missing link between formulation chemistry and real-world spray behaviour.
Utilising bubble pressure tensiometry, we can replicate the millisecond timescales relevant to atomisation, offering deeper insights into surfactant kinetics and their role in delivering consistent and enhanced spray performance. If you want to achieve the perfect mist and wetting in a single trigger pull, understanding how your formulation behaves dynamically is key. Contact us to learn more about how our dynamic surface tension analysis services can help to optimise your surface spray formulations.

Related Article;
Dynamic Insights for a Sustainable Clean – The Future of Surfactant Performance in Detergency
Understanding the Effects of Temperature on Surface Tension
Wasif Altaf serves as an Applications Specialist at the Centre for Industrial Rheology, leveraging a chemical engineering background (BEng) to bridge theory and practice. His work focuses on advanced rheological characterisation.
